In the ever-evolving world of interior design and construction, materials are constantly being refined to meet the demands for sustainability, durability, and aesthetic appeal. One such material that has gained significant traction in recent years is the prelaminated medium-density fiberboard (MDF). This blog post will delve into the world of prelaminated MDF, discussing its definition, benefits, and various applications in the industry.
What is Prelaminated MDF Board?
Medium-density fiberboard, commonly known as MDF, is an engineered wood product made by breaking down hardwood or softwood residuals into wood fibers and combining them with a resin binder. Prelaminated MDF refers to MDF boards that have a layer of decorative laminate applied to one or both sides during the manufacturing process. This laminate can come in a variety of finishes, including wood grain, solid colors, and even high-gloss or metallic effects.
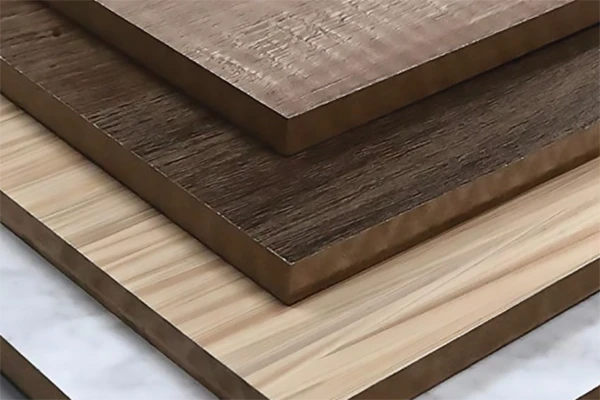

Advantages of Prelaminated MDF:
Aesthetics: The pre-applied laminate offers a wide range of design options, allowing for a seamless and consistent finish without the need for additional painting or staining.
Durability: The laminate surface is resistant to scratches, stains, and moisture, making it ideal for high-traffic areas and wet environments like kitchens and bathrooms.
Cost-Effective: Compared to solid wood, prelaminated MDF is more affordable, providing a cost-effective solution for large-scale projects without compromising on quality.
Easy to Work With: MDF is easy to cut, shape, and assemble, making it a favorite among both professional woodworkers and DIY enthusiasts.
Sustainability: MDF is made from wood fibers that are a byproduct of other manufacturing processes, contributing to a more sustainable use of resources.
Applications of Prelaminated MDF:
Furniture Making: Used for creating cabinetry, shelving, and decorative pieces that require a polished look without the high cost of solid wood.
Wall Paneling: Its uniform appearance and durability make it an excellent choice for wall panels that need to withstand daily wear and tear.
Office Furniture: Desks, partition panels, and storage units in office spaces often utilize prelaminated MDF for a professional and long-lasting finish.
Store Fixtures: Retail environments benefit from the material’s ability to maintain its appearance over time, with less maintenance required.
Architectural Millwork: Used in various architectural details such as wainscoting, baseboards, and crown moldings for a consistent and refined look.
Future Outlook:
As the construction and design industries continue to push for materials that are both sustainable and stylish, prelaminated MDF is poised to play a significant role. Its versatility, coupled with the growing range of laminate designs, ensures that prelaminated MDF will remain a popular choice for years to come.
Conclusion:
Prelaminated MDF board is a testament to the innovation in material science, offering a blend of functionality, affordability, and style. As designers and builders continue to explore its potential, we can expect to see even more creative and practical uses for this dynamic material in the future.
For more insights into the world of design and construction materials, stay tuned to our blog. And for those looking to incorporate prelaminated MDF into their next project, consider reaching out to your local suppliers to discuss the possibilities.
Post time: 05-11-2024